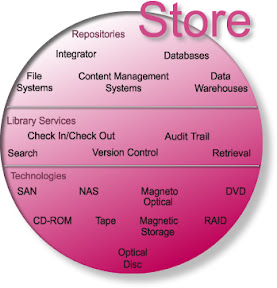
The Store Module determines where the content goes and how it can be located. The Store Module is used for the temporary or transient storage of information, which it is not required or desired to archive. Even if it uses media that are suitable for long-term archiving, “Store” is still separate from “Preserve.” These infrastructure components are sometimes held at the operating system level like the file system, and also include security technologies, which will be discussed farther below in the “Deliver Module” area. However, security technologies including access control are super-ordinate components of an ECM solution. The “Store Module” can be divided into three categories:
Repositories; Repositories are a place that is usually a file system, database or data warehouse where content is deposited or stored. The storage locations have different kinds of repositories that can be used in combination with any transient content per location.
File systems; The way in which files are named and where they are placed logically for storage and retrieval, most commonly in a hierarchical (tree) structure.
Integrator; Integrator is a technological function that makes content into a whole by bringing all repositories together; to make or become a single repository for the process of unifying or uniting. Has the ability to connect multiple repositories across the functional model.
Content Management Systems; Content management systems have the capability to manage and track the location of, and relationships among, content within multiple repositories.
Database; The term database originated within the computer industry. Although its meaning has been broadened by popular use, even to include non-electronic databases, this article takes a more technical perspective. A possible definition is that a database is a collection of records stored in a computer in a systematic way, so that a computer program can consult it to answer questions. The items retrieved in answer to queries become information that can be used to make decisions. The computer program used to manage and query a database is known as a database management system (DBMS). The properties and design of database systems are included in the study of information science. Is defined as; Electronic collection of records stored in a central file and accessible by many users for many applications and a collection of data elements within records or files that have relationships with other records or files. Relational databases are most common—data is stored in standard rows, tables, and columns. XML and Ontology Web Language (OWL) databases are a developing technology.
Data Warehouse; Data Warehouse is the central repository for all, or most, of an organization’s structured data with the next generation of database vendors accepting the need to unite both structure and unstructured content into one environment. ECM interacts with this environment and through business requirements are loosely connected.
Storage Technologies; Storage technologies a wide variety of technologies can be used to store information, depending on the application and system environment.
Storage Area Network (SAN)/ Network Attached Storage (NAS); the NAS can be part of a SAN with hard disk storage directly attached to the network to provide information access. The SAN is a high-speed network that connects computer systems and storage elements and allows movement of data between computer systems and storage elements and among storage elements.
Paper; although Electronic Content Management systems are considered essential for streamlining paper-intensive operations, paper is still required for some operations, and in some industries, paper must be stored for a certain period of time for legal reasons, regulatory mandates, etc. However, once the data has been captured and the image stored, paper documents can be archived away from the central office in special warehouses, thus reducing the direct cost of storage but increasing the cost of retrieval (if the physical paper is frequently required).
Paper is generally a low cost option for storage for low volume businesses. However, as paper volume increases, the cost of manual paper processes and storage also increases. In some cases, these costs become a limiting factor to growth in a company.
Compact Disc Read Only Memory (CD-ROM) and, Digital Versatile Disc (DVD); CD-ROM optical disc is created by a mastering process and used for distributing read-only information. The DVD is a 120 mm optical disc on which digital video, audio, data, and images can be stored. The available formats are read-only, recordable, and rewritable.
Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID); RAID storing is the same data on multiple hard disks for improved performance and fault tolerance.
Magnetic Storage/Optical; During the initial period that an image is being used for work processing, it is frequently accessed for different operations and stored temporarily on different magnetic media. Images are generally stored on the host system, and as the application dictates, they are downloaded to workstations for work processing. Once on the workstation, the size of the document or document folder, number of documents, and the need to access those documents quickly will help determine the workstation memory requirements.
Optical Disk; Optical disk storage is commonly used to store or archive images once the initial work has been completed. Images are downloaded from magnetic disk to optical disk storage, making the magnetic disk available for new batches of images. An optical storage configuration is similar to a magnetic disk configuration. The size of the image database is dependent on the estimated total number of images to be stored, the frequency of access, the response time requirements for access, and the DPI of the image. Depending on the application needs, optical storage can range from one stand-alone optical disk drive with image platters manually inserted as needed to machines with multiple disk drives that automatically retrieve disks and insert them into the drives. Optical disk storage devices and optical disks are available in a variety of sizes and configurations. Depending on the configuration, vendors could propose different optical disk technologies.
Library Services; have to do with libraries only in a metaphorical way. They are the administrative components close to the systems that handle access to information. The Library service is responsible for taking in and storing information from the “Capture module” and any managing components within “Manage Module”. The storage location is determined only by the characteristics and classification of the information. These services are used and leveraged across all compartmentally management component’s along with capture and deliver modules. The library service works in concert with the database of the manage components each support the following functionalities:
Search; typically has core ties into stored content according to its content type from both the structured and now un-structured data. Having the ability to reference content where it is held in any system, catalogue information in a database, letters and reports in content management systems. However, for an individual to perform a business tasks efficiently, they need to access all relevant content at once. A complaint from a customer will appear in the letters document management system, but that customer's details are hidden in the CRM application and without understanding the product they bought (information that is held in the Products database) it will be difficult to help them. Searching is the act of trying to find something or someone. One can distinguish between two forms of search. One may search for an item that is known to exist, with the intent to locate it, and one may search for an item whose existence is uncertain, in order to ascertain whether it exists or not. The ability to locate the correct and proper content within a repository indexed by either within a database or reference.
Version Control; the ability to track and manage the history of a particular piece of content may be very important. Some of the features to look for may include: the ability to rollback to a previous version of a document, that ability to track major and minor revisions of a document, and the ability to purge earlier versions of a document. The ability to track the history, implement rollback activities on content at any level either directly/indirectly to the physical document through the Information Life-cycle Process (ILcP).
Check In/Check Out; systems used in a manner that require users to “check out” documents must ensure that modifications are made by one person at a time. Another potential feature that may need to be evaluated is if the user is disconnected from the system can they modify the document and have resulting changes synchronized with the document stored in the repository. Checking in and out ensures that only one person can work on a document at any time.
Workflow; compartmental operational function executing specific operations of the smallest actionable item of a business function. This area operates within an any area of the ECM module and should not to be confused with the holistic process orchestration of Business Process Management.
Retrieval; the outlined requirements for accessing the repository from any device or workstation requests must be serviceable and separate from other modules. Access is through the Internet, and via service requests utilizing an OWL, XML or API based on international standards.
Audit Trail; knowing where a document is or has been is vital to ensuring only entitled users have had access to content. The inherent ability to also track content externally is becoming needed for accountability check and balances. This function provides an accurate logging of who accessed, changed content and when for accountability. The Audit Trail is an examination and verification of a company's accounting records and supporting documents by a professional, such as a Certified Public Accountant (CPA). An audit trail is the step-by-step accounting or record from/by/which data can be traced to its source.
No comments:
Post a Comment