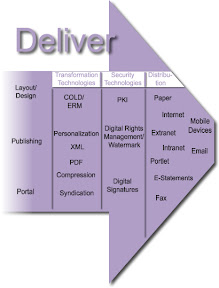
The Deliver module determines how to get the right content to the right audience on the correct device. The deliver module for ECM is used to present information from manage, store and preserve modules. They also contain functions used to enter information in systems (such as information transfer to media or generation of formatted output files) or for readying (for example converting or compressing) information for the store and preserve components. The functionality in the deliver module is also known as “output” and summarized under the term “Output Management.” The deliver module comprises of three groups for functions and media: Transformation Technologies, Security Technologies, and Distribution. Transformation and Security as services belong on the middleware level and should be available to all ECM components equally.
Layout/Design; Visually, there is very little originality in design — it is the rearrangement of an idea observed and recorded previously. No matter how simple the design may be, there are certain principles that must be applied. Appreciation of their importance will be slowly gained by observation and practice together with good judgment. Principles of design should always be incorporated in any graphic design project to assist its communicating and graphic interest, however in the planning of a basic design; the designer must produce a job to suit the class of work, the copy, and the tastes of the business. To develop a senses of design use the three “eyes”; Visual-eyes: examine closely all types of printed material; Critic-eyes: separate the good from the bad; Analyst-eyes: select the element that makes it a good design. There are three essential qualities needed; Vision — to be able to detect an idea and then to contemplate the idea; Imagination — to be able to use an idea effectively; Judgment — to be able to assess the idea's value, correct place, and use; Balance — this is the result of an arrangement of one or more elements in the design so that visually, they equal each other.
Publishing; Publishing is the industry of the production of literature or information - the activity of putting information for public view. Traditionally, the term refers to the distribution of printed works such as books and newspapers. With the advent of digital information systems and the Internet, the scope of publishing has expanded to include websites, blogs, and other forms of new media. As a business, publishing includes the development, marketing, production, and distribution of news and non-fiction magazines and books, literary works, musical works, software, other works dealing with information.
Portal; The simplest definition is a door or entrance; specificity is required for ECM. Portal is a web site that is the entry point to both the Internet and Intranet services. A portal offers functionality in the areas of: search, personalization, aggregation and all abstract business processes leveraging portlets as the core for aggregating information at this presentation layer.
Portlet; A portlet is a small chunk of secondary content that is often assisting or functional, like a navigation or information on related items. Most of the time they grace one of the two columns that are available on most sites. This does seem to indicate that portlets are a subtype of pagelets but for various usage reasons it’s generally beneficial to regard them as separate and simply include portlets using a pagelet.
Transformation Technologies; Transformation is a form of conversion in which a file is converted into a file format with a comparable structure (examples, OWL to XML, XML to OWL, XML to XML, or SGML to HTML) and is the changing of content from one format to the needed delivery format.. Usually, this form of conversion can be carried out very well. However, it can lead to the usual problems, since in many cases such a conversion is used to increase the quality of the files, based on the principle that 'we are at it anyway'.
COLD/ERM; COLD/ERM is the way documents and delivered from computer output (reports primarily) from magnetic disks, optical discs, and magnetic tape. Once the document has been stored, the reports can be distributed for viewing, printing, faxed, or distributed via a web interface for both or either Internet/Intranet. Often used for Internet customer facing applications and processes. Enterprise Report Management (formerly known as COLD technology, and, today, often written as COLD/ERM): A component technology of an ECM environment. This technology electronically stores, manages, and distributes documents that are generated in a digital format and whose output data are report-formatted/print-stream originated. Unfortunately, documents that are candidates for this technology too often are printed to paper or microform for distribution and storage purposes. This is mostly an aged terminology which over time will collectively assimilate into the “Document Management” functional model.
Personalization; Dynamic content automatically assembles the appropriate content to deliver personalized content which specifically meets user needs. User content actions and requests can be used to predict the content requirements. Personalization techniques currently in use include Personal records in a database/file, Rule base or a profile database, Data mining (of numerical and string data in formatted tables/files), Web-log data is stored in formatted tables/files, Text mining, Online analytical processing (OLAP) techniques.
XML; XML is an established standard, based on the Standard Generalized Markup Language, designed to facilitate document construction from standard data items. Also used as a generic data exchange mechanism. XML is a W3C initiative that allows information and services to be encoded with meaningful structure and semantics those computers and humans can understand. XML is great for information exchange, and can easily be extended to include user-specified and industry-specified tags.
OWL; Ontology Web Language (OWL) is a markup language for publishing and sharing data using ontologies on the Internet. OWL is a vocabulary extension of the Resource Description Framework (RDF) and is derived from the DAML+OIL Web Ontology Language (see also DAML and OIL). Together with RDF and other components, these tools make up the Semantic Web project.
PDF; Portable Document Format (PDF) is an open file format created and controlled by Adobe Systems, for representing two-dimensional documents in a device independent and resolution independent fixed-layout document format. Each PDF file encapsulates a complete description of a 2D document (and, with the advent of Acrobat 3D, embedded 3D documents) that includes the text, fonts, images, and 2D vector graphics that compose the document. PDF files do not encode information that is specific to the application software, hardware, or operating system used to create or view the document. This feature ensures that a valid PDF will render exactly the same regardless of its origin or destination (but depending on font availability when fonts are not encapsulated in the file).
Compression; image compression can be lossy or lossless. Lossless compression is sometimes preferred for artificial images such as technical drawings, icons or comics. This is because lossy compression methods, especially when used at low bit rates, introduce compression artifacts. Lossless compression methods may also be preferred for high value content, such as medical imagery or image scans made for archival purposes. Lossy methods are especially suitable for natural images such as photos in applications where minor (sometimes imperceptible) loss of fidelity is acceptable to achieve a substantial reduction in bit rate. Methods for lossless image compression are; Run-length encoding; Entropy coding; Adaptive dictionary algorithms such as LZW. Methods for lossy compression; reducing the color space to the most common colors in the image. The selected colors are specified in the color palette in the header of the compressed image. Each pixel just references the index of a color in the color palette. This method can be combined with dithering to blur the color borders. Chroma sub sampling. This takes advantage of the fact that the eye perceives brightness more sharply than color, by dropping half or more of the chrominance information in the image. Transform coding. This is the most commonly used method. A Fourier-related transform such as DCT or the wavelet transform are applied, followed by quantization and entropy coding. Fractal compression.
Syndication; Syndication is in which a section of a website is made available for other sites to use. This could be simply by licensing the content so that other people can use it; however, in general, web syndication refers to making Web feeds available from a site in order to provide other people with a summary of the website's recently added content. This originated with news and blog sites but is increasingly used to syndicate other types of information. Millions of online publishers including newspapers, commercial web sites and blogs now publish their latest news headlines, product offers or blog postings in standard format news feed. Syndication benefits both the websites providing information and the websites displaying it. For the receiving site, content syndication is an effective way of adding greater depth and immediacy of information to its pages, making it more attractive to users. For the transmitting site, syndication drives exposure across numerous online platforms. This generates new traffic for the transmitting site — making syndication a free and easy form of advertisement. The prevalence of web syndication is also of note to online marketers, since web surfers are becoming increasingly wary of providing personal information for marketing materials and expect the ability to subscribe to a feed instead.
Security Technologies; with the rapid growth of interest in the Internet, network security has become a major concern to companies throughout the world. The fact that the information and tools needed to penetrate the security of corporate networks are widely available has increased that concern.
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI); PKI enables users of an unsecured public network such as the Internet to securely and privately exchange data and money through the use of a public and a private cryptographic key pair that is obtained and shared through a trusted authority. The public key infrastructure provides for a digital certificate that can identify an individual or an organization and directory services that can store and, when necessary, revoke the certificates. Although the components of a PKI are generally understood, a number of different vendor approaches and services are emerging. Meanwhile, an Internet standard for PKI is being worked on.
Digital Rights Management (DRM)/Watermark; DRM is the umbrella term referring to any of several technologies used to enforce pre-defined limitations on software, music, movies, or other digital data. In more technical terms, DRM handles the description, layering, analysis, valuation, trading and monitoring of the rights held over a digital work. In the widest possible sense, the term refers to any such management. Watermark is a translucent design visible in handmade paper when held up to the light. Watermark designs were typically wired into the paper mold, and can denote either the size of the paper, the place of manufacture, or the intended market. Typically the watermark is present in the center of the right side of the paper mold.
Digital Signature; Digital signature is like a paper signature, but it is electronic. A digital signature cannot be forged. A digital signature provides verification to the recipient that the file came from the person who sent it, and it has not been altered since it was signed.
Distribution technologies leveraging
Mobile Device; Devices that are not directly connected into the network via a “hard-line”, an example of these types of devices would possible be all wireless connected devices. Mobile Devices or Handheld devices (also known as handhelds) are pocket-sized computing devices that are rapidly gaining popularity as the access to information in every walk of life becomes more and more mission critical. Along with mobile computing devices such as laptops and smart hones, and PDA’s represent the new frontier of computing as desktop computers find less and less favor among every day users. The following are typical handhelds such as: Information appliance, Smart phone, Personal digital assistant, Mobile phone and Handhelds.
Internet; The Internet, or simply the Net, is the publicly accessible worldwide system of interconnected computer networks that transmit data by packet switching using a standardized Internet Protocol (IP). It is made up of thousands of smaller commercial, academic, domestic, and government networks. It carries various information and services, such as electronic mail, online chat, and the interlinked Web pages and other documents of the World Wide Web. Contrary to some common usage, the Internet and the World Wide Web are not synonymous: the Internet is a collection of interconnected computer networks, linked by copper wires, fiber-optic cables, etc.; the Web is a collection of interconnected documents, linked by hyperlinks and URLs, and is accessible using the Internet.
Intranet; The Intranet is a private network that uses Internet Protocols, network connectivity, and possibly the public telecommunication system to securely share part of an organization's information or operations with its employees. Sometimes the term refers only to the most visible service, the internal website. The same concepts and technologies of the Internet such as clients and servers running on the Internet protocol suite are used to build an intranet. HTTP and other Internet protocols are commonly used as well, especially FTP and email. There is often an attempt to use Internet technologies to provide new interfaces with corporate 'legacy' data and information systems. There does not necessarily have to be any access from the organization's internal network to the Internet itself. Where there is, there will usually be a firewall with a gateway through which all access takes place, along with user authentication, encryption of messages, and the use of virtual private networks (VPNs) that tunnel through the public network. Through such devices, company information and computing resources can be shared by employees working from external locations. Increasingly, intranets are being used to deliver tools and applications, e.g.: collaboration (to facilitate working in groups and for teleconferences) or sophisticated corporate directories, sales and CRM tools, project management, etc, to advance productivity. Intranets are also being used as culture change platforms. For example, in IBM's "Jam" program, large numbers of employees could discuss key issues in online forums, and key ideas surfaced with the aid of text analysis tools. Intranet traffic, like public-facing web site traffic, is better understood by using web metrics software to track overall activity, as well as through surveys of users. Intranet User Experience, Editorial, and Technology teams work together to produce in-house sites.
Extranet; The extranet is a private network that uses Internet protocols, network connectivity, and possibly the public telecommunication system to securely share part of a business's information or operations with suppliers, vendors, partners, customers or other businesses. An extranet can be viewed as part of a company's Intranet that is extended to users outside the company (e.g.: normally over the Internet). It has also been described as a "state of mind" in which the Internet is perceived as a way to do business with other companies as well as to sell products to customers. An argument has been made that "extranet" is just a buzzword for describing what institutions have been doing for decades, that is, interconnecting to each other to create private networks for sharing information.
Paper; Paper is still required for some operations, and in some industries, paper must be distributed for a certain legal reasons, regulatory mandates, etc.
eStatements; eStatements are a convenient way to access monthly account statements online, and replaces the paper statement sent through the mail. eStatements provide an environment where the paper statement is no longer required. Instead, it can be viewed online or received through email. It can be available by the same business day and quicker than mailed statements. eStatements are an electronic version of the paper statement. Using a current email address, a monthly statement notification automatically delivered directly to the email inbox! A statement can be accessed anytime, day or night through the online environment. An eStatement is an exact replica of the paper statement and contains the identical information. 97% of eStatement adopters continue to receive a paper statement. Firms must wean customers from their addiction to paper by offering a printable statement in PDF format, automatically turning off paper statements for eStatement adopters, and charging customers who request a paper statement via snail mail.
Digital replica of the original statement paper version, and available via an online service or email to authorized users.
Portal; Portals are pages intended to serve as "main pages" for specific topics or areas. Web portals are sites on the World Wide Web that typically provide personalized capabilities to their visitors. They are designed to use distributed applications, different numbers and types of middleware, and hardware to provide services from a number of different sources. In addition, business portals are designed to share collaboration in workplaces. A further business-driven requirement of portals is that the content be able to work on multiple platforms such as personal computers, personal digital assistants (PDAs), and cell phones.
Facsimile (FAX); FAX is a method of sending graphical data down a serial communication system (usually a telephone line or intranet) that involves (conventionally) scanning a document at one end, transmitting the data via modulated tones and then reproducing the picture at the other end on heat-sensitive paper, printers or computers. Fax modems to allow computer-generated graphics to be transmitted as if they came from a conventional fax. A computer and fax modem can be used to receive a fax transmission regardless of origination. It can be display it on the screen and/or output it via a conventional printer or route into other technologies for processing. A fax machine is essentially an image scanner, a modem, and a computer printer combined into a highly specialized package. The scanner converts the content of a physical document into a digital image; the modem sends the image data over a phone line, network and the printer at the other end makes a duplicate of the original document. Fax machines with additional electronic features can connect to computers can be used to scan documents into a computer, and to print documents from the computer. Such high-end devices are called multifunction printers and cost more than fax machines. Capabilities, there are several different indicators of fax capabilities: Group, class, data transmission rate, and conformance with ITU-T (formerly CCITT) recommendations.

No comments:
Post a Comment